Heat exchangers
 Plate-type heat exchanger
Plate-type heat exchanger
There are some specific characteristics in plate-type heat exchanger using. Heat transfer through plates instead of tubes. Turbulent flow at low velocity produces high heat transfer efficiency and low fouling. The result…compact units with small heat transfer areas compared to conventional shell & tube exchangers. Plate exchangers conserve both material and labor resources, reducing up-front costs and future operational costs.
Spiral-type heat exchanger

Heating or cooling of particle-laden or viscous fluids is a difficult duty for most types of heat exchangers. Spiral heat exchangers with their compact, single channel design are ideally suited for outstanding thermal and uptime performance in these duties. Spirals can attain high heat-transfer coefficients with particle-loaded fluids, while avoiding fouling, plugging, unequal fluid distribution or dead spots in both channels. Other significant duties involve vapor/liquid and gas or vapor/liquid service where the spiral’s subcooling capability and long condensation path maximizes recovery.
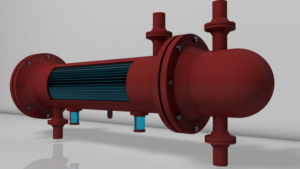 Shell-and-tube heat exchanger
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers are one of the most popular types of exchanger due to the flexibility the designer has to allow for a wide range of pressures and temperatures. Typically found in applications where a need to heat or cool large volumes exists; however small volume applications are also very common. Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are used widely in the chemical process industries, especially in refineries, because of the numerous advantages they offer over other types of heat exchangers. Condensation or boiling heat transfer can be accommodated in either the tubes or the shell, and the orientation can be horizontal or vertical. Condensation or boiling heat transfer can be accommodated in either the tubes or the shell, and the orientation can be horizontal or vertical, and cleaning and repair are relatively straightforward.
Vessel equipment
 Pressure vessels
Pressure vessels
Pressure vessels are widely used in the chemical and energy industries. Various types of pressure vessels (such as boilers, pressure chambers, receivers, cisterns and tanks) are used to form integral part of the oil-and-gas production plants. Special drums are intended to transport or storage of pressurized and liquid gas, fluids and granular materials.
Pressure vessel operating deals with a high risk, that’s why using of this equipment is always under law regulations and public supervision. It is recommended to acquire only well-established manufacturer’s pressure vessels, and to cooperate only with highly skilled specialists.
Eco Power Company provides you both sides!
 Tanks
Tanks
Storage tanks are used in the energy sector, especially for oil storage. There is wide range of tanks: land, underground and underwater. Or they can also be classified according to the material of manufacture metal, reinforced concrete and synthetic.
Usually tanks with capacity less than 50 m3 are made at manufacturer’s plants. When being assembled tanks shall be equipped with some optional or missing equipment. Those big tanks with capacity up to 100 000 m3 are usually transported as a number of prefabricated parts to the facilities, and then shall be collected into accumulator tank (for example, vertical metal tanks). Special applications might require tanks to be rectangular, in the form of horizontal cylinders, or even spherical in shape. Horizontal cylinders and spheres are generally used for full pressure storage of hydrocarbon or chemical products.
Tanks can have different sizes, ranging from 2 to 60 m diameter or more. They are generally installed inside containment basins in order to contain spills in case of rupture of the tank.
 Scrubbers
Scrubbers
Scrubbers are air pollution control devices that use liquid to remove particulate matter or gases from an industrial exhaust or flue gas stream. This atomized liquid (typically water) entrains particles and pollutant gases in order to effectively wash them out of the gas flow. In comparison to other air pollution control devices, scrubbers are very multidisciplinary, with the ability to remove solids, mists, and gases simultaneously while also providing cooling. They are also capable of handling explosive and flammable gases safely.
Scrubbers can handle flammable and explosive dusts with little risk. This device provides gas absorption and dust collection in a single unit, and also provides cooling of hot gases. It is compact; can often be retrofitted into existing collection systems. Corrosive gases and dusts can be neutralized.
 Separators
Separators
An oil/gas separator is a pressure vessel used for separating a well stream into gaseous and liquid components. They are installed either in an onshore processing station or on an offshore platform.
Based on the vessel configurations, the oil/gas separators can be divided into horizontal, vertical, or spherical separators. In teams of fluids to be separated, the oil/gas separators can be grouped into gas/liquid two-phase separator or oil/gas/water three-phase separator. Based on separation function, the oil/gas separators can also classified into primary phase separator, test separator, high-pressure separator, low-pressure separator, deliquilizer, degasser, etc.
To meet process requirements, the oil/gas separators are normally designed in stages, in which the first stage separator is used for priliminary phase separation, while the second and third stage separator are applied for further treatment of each individual phase (gas, oil and water). Depending on a specific application, oil/gas separators are also called deliquilizer or degasser. The deliquilizers are used to remove dispersed droplets from a bulk gas stream; while the degassers are designed to remove contaimined gas bubbles from the bulk liquid stream.
